The advantages and disadvantages of using fresh, frozen or chilled Semen
FRESH Semen Insemination.
Fresh semen insemination is the process by which the stallion is collected using and artificial vagina, assessed and possibly mixed with an extending medium and inseminated immediately into the mare.
Advantages
- decreased risk of injury to both mare and stallion
- useful when there is a size discrepancy between the mare and stallion (ie pony stallion covering a thoroughbred mare)
- allows assessment of the semen prior to insemination in the mare
- stallions with poor quality semen can have extender added to the semen prior to insemination and therefore increasing the viability of the semen and increasing conception rates
- decreased risk of disease transmission
- one collection from the stallion can be split and used for multiple mares at one time
Disadvantages
- More expensive than natural cover
- Both the mares and stallion have to be present at the same facility at the same time
- The semen is only viable outside of the body for a short period therefore the insemination needs to take place within a very short time of collection and cannot be transported.
Chilled Semen Insemination
Chilled semen is the process by which the semen is collected from the stallion using an artificial vagina and then processed with an extending medium that acts to protect the semen. Once the semen has been evaluated and extended it is chilled down at a rate of 0.3oC every minute until it reaches a temperature of 4-6oC Once the semen is held at this temperature it us usually viable for up to 72 hours. The semen is removed from the sealed container holding it at temperature and inseminated immediately into the mare, a small drop is kept aside to be assessed for motility and viability after the mare is inseminated.
Advantages
- The semen can be transported to another facility and interstate increasing the breeders choice of stallion without having to transport the mare
- The cost of processing and transporting chilled semen is lower than the processing and transport costs associated with frozen semen
- The semen is more viable than frozen semen when inseminated into the mare therefore the time window around ovulation in which the mare can be inseminated is longer. This reduces the need for multiple follicle tests and intern reduces cost.
- Higher expected rates of conception as compared to frozen semen insemination
- Lower overall cost to the mare owner
Disadvantages
- The semen is only viable for 72 hours after collection so it cannot be transported long distances or to remote areas without considerable cost.
- The stallion may not be available for collection when the mare is ready to ovulate meaning a whole cycle can be missed
- Semen cannot be transported internationally therefore decreasing the stallion choice available to the mare owner.
- Most couriers don’t deliver on weekends … mares do not know this!!
- Communication between the mare owner, stallion owner and their associated veterinarians needs to be well coordinated to ensure that the stallion is available to collect and ship in time for the mare’s ovulation.
- Some stallion’s semen does not chill and transport well and this should be checked by the mare owner as to whether the stallion freezes or chills better.
Frozen semen
This is the process by which the stallion is collected using an artificial vagina and the semen is processed and stored in liquid nitrogen at -196oC.
Advantages
- The semen lasts indefinitely in liquid nitrogen so genetics can be stored for many years.
- Frozen equine semen can be transported all over the world and stored at your breeding facility for any time your mare may require it.
Disadvantages
- Some equine semen does not freeze well resulting in very low post thaw fertility rates
- Equine semen does not live very long post thaw so must be inseminated into the mare as close to ovulation as possible resulting in more frequent scanning of the mare and therefore increased mare costs
- The conception rates with frozen semen are much lower than for chilled or fresh semen insemination
Preparation for Foaling
The best way to be ready and prepared for your foals arrival is to have a foaling kit packed and easily accessible when needed. Its also not a bad idea to print the list, laminate and stick to the lid of your box so that it can be easliy repacked for the next foaling. We recommend the following contents for your foaling kit
- Record Book
- Tail Bandage
- Gloves
- Waterproof clothing
- Lubrication
- Ropes
- Dilute iodine solution
- Dipping Container
- Fleet® enema
- Baling Twine
- Towels
- Twitch
- Warm water
- Bucket or Bag For Placenta
- Phone
- Scissors
- Bridle / Lead
- Torch
How to identify when your unborn foal may be in trouble “foetal distress”
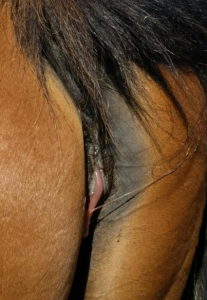
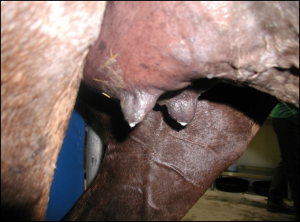
The following two images are the most common mare signs of foetal distress. If you notice these in your mare then it is time to call your vet immediately.
1. Vulvar discharge
2. Early Mammary development or running milk
The new born foals Rule of 1-2-3
One of the best rules to follow in relation to newborn foals it the rule of 1-2-3 as early intervention results in better outcomes for both the mare and foal
1. The foal is standing within 1 hour of birth
2. The foal nurses within 2 hours of birth
3. After birth passes within 3 hours of birth
If your mare and foal do not follow the rule of 1-2-3 then it is time to call your vet